
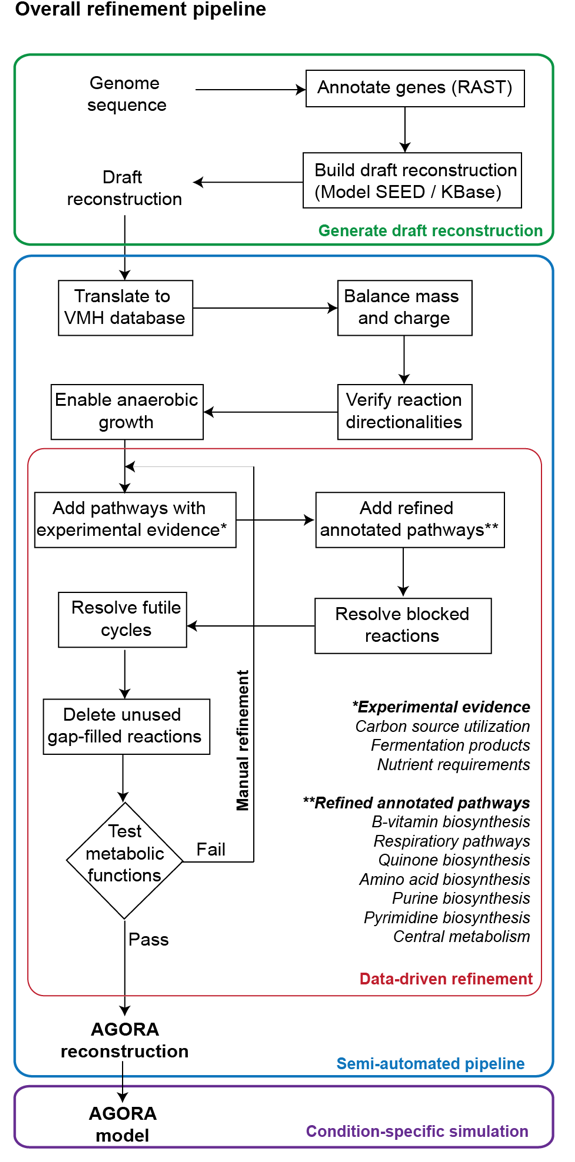


The gut microbiome resource contains the collection of over 800 semi-automatically curated strain-specific metabolic reconstructions, belonging to 205 genera and 605 species [1].
These gut microbial, genome-scale metabolic reconstructions have been generated based on draft reconstructions obtained from ModelSeed [2] or the KBase, and subsequently manual curated against available biochemical and physiological literature. We developed a novel reconstruction paradigm, which allowed us to accelerate the reconstruction process substantially. In this reconstruction paradigm, we applied improvements and modifications identified to be needed for one draft reconstruction to other reconstructions with the same issue (see Figure). All reconstructions have been subjected to the same quality-control and -assurance measures developed for high-quality, genome-scale metabolic reconstructions [3].
Beside extensive literature review, including more than 200 primary and review articles, we also included information from microbiology textbooks, most notably Bergey's manual [4]. Importantly, the collected information can be also retrieved from the Gut microbiome resource (here.
Genome-scale metabolic reconstructions rely heavily on an organism's genome annotation. Consequently, we performed extensive refinement of all microbial genome annotations that were present in the PubSeed database [5].
Overall, all microbial reconstructions were based on literature-derived experimental data and/or comparative genomics. A typical reconstruction contains an average of 771 (±262) genes, 1198 (±241) reactions, and 933 (±139) metabolites. We provide detailed information for each strain and reconstruction along with known fermentation products and carbon sources.
As with the human metabolic reconstruction, each microbial metabolic reconstruction is amenable to computational modeling, e.g., using the COBRA toolbox [6]. Each metabolic model, or the entire collection, can be downloaded here.
We are continuously updating, improving, and expanding this resources and welcome your feedback and suggestions (e.g., microbes, pathways to be added).
References
When using one, multiple, or all microbial metabolic reconstruction, their content, or the downloaded version, please cite:
Magnusdottir et al, "Generation of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions for 773 members of the human gut microbiota", Nature Biotechnology, 35(1):81-89 (2017). doi:10.1038/nbt.3703